이제 드디어 스프링을 해 볼 차례다 !!
일단 계산기, 로또로 다져진 실력을 레이싱카 미션에 적용시켜 보았다. 결론부터 말하자면 실력이 많이 늘었다는게 느껴질 정도였다. 쉬웠음!!

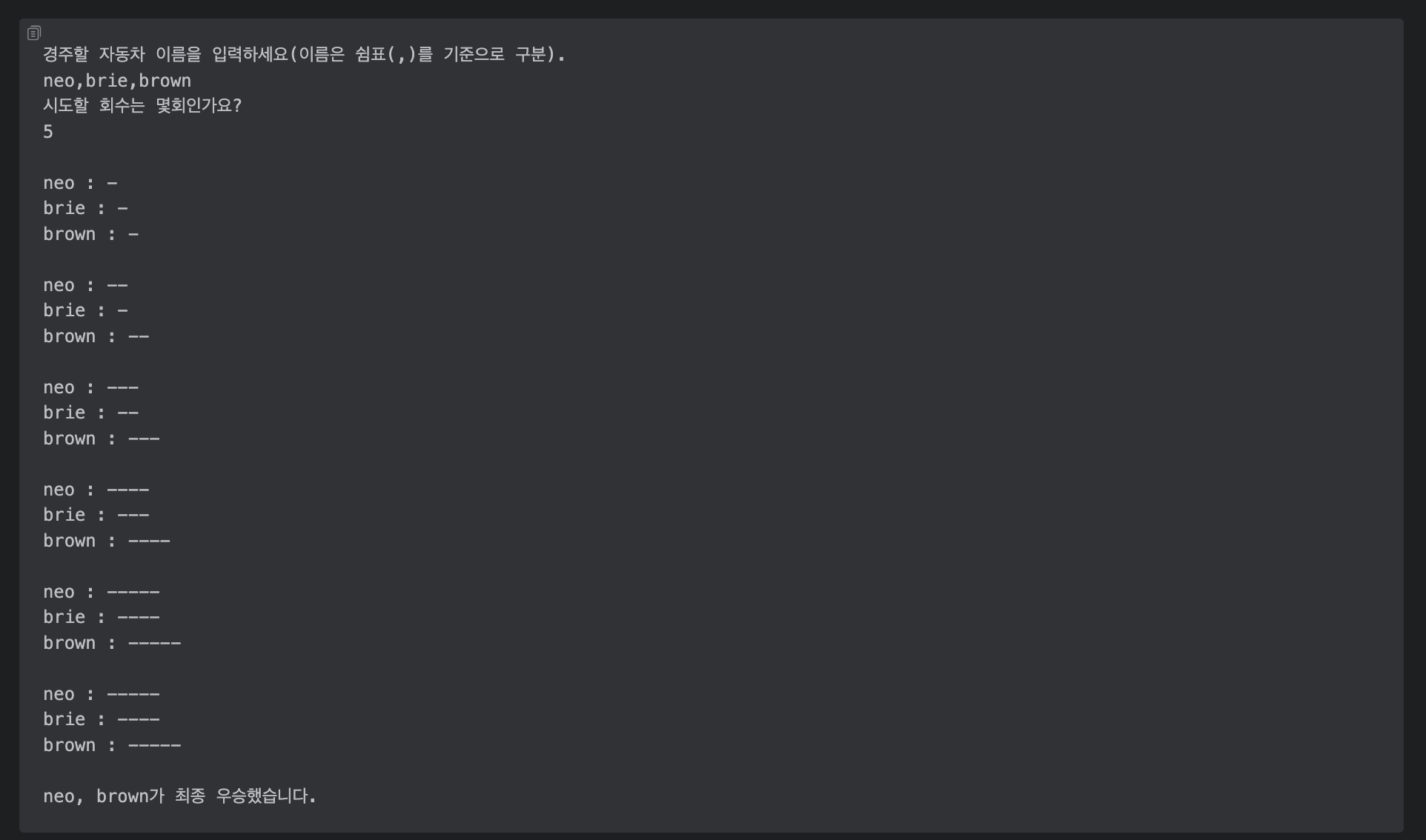
일단 문제 조건은 요렇다.
그리구 내 패키지 구조
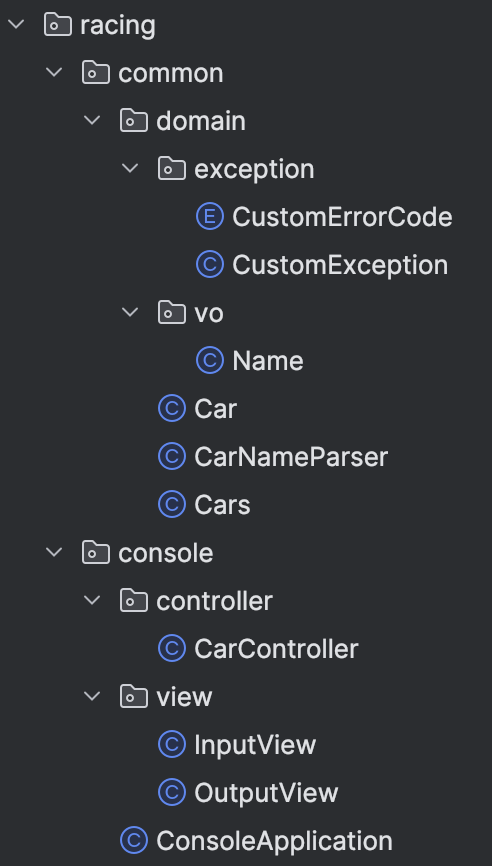
이제 내가 작성한 코드를 소개해보겠다.
*exception 패키지 - CustomException은 여기서 처음 구현해보았다. 정석적인 CustomException은 아님.
- CustomErrorCode
package com.racing.common.domain.exception;
public enum CustomErrorCode {
EXCEPTION_RANGE("차 이름 너무 긺"),
EXCEPTION_CAR("차 없음");
private final String message;
CustomErrorCode(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
}
enum으로 관리해서 메세지만 넘겨주도록 만들었음!
- CustomException
package com.racing.common.domain.exception;
public class CustomException extends RuntimeException{
public CustomException(CustomErrorCode customErrorCode) {
super(customErrorCode.getMessage());
}
}
RuntimeException 상속받아서 CustomErrorCode에서 메세지만 전달받도록 작성했다.
* vo 패키지
- Name
package com.racing.common.domain.vo;
import com.racing.common.domain.exception.CustomErrorCode;
import com.racing.common.domain.exception.CustomException;
public class Name {
private static final int CAR_NAME_BOUNDARY = 5;
private final String name;
public Name(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public static Name from(final String name) {
validateNameRange(name);
return new Name(name);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
private static void validateNameRange(String name) {
if (name.length() > CAR_NAME_BOUNDARY) {
throw new CustomException(CustomErrorCode.EXCEPTION_RANGE);
}
}
}
차 이름 하나 하나를 원시값 포장해줌. 여기서 static 메서드를 통해 검증까지 한 후 값 포장해줄 수 있도록 코드 작성하였다.
- Car
package com.racing.common.domain;
import com.racing.common.domain.vo.Name;
import com.racing.web.random.CreateRandomNumber;
public class Car {
private static final int CAR_MOVE_BOUNDARY = 4;
public int moveCount;
private final Name carName;
public Car(int moveCount, String carName) {
this.moveCount = moveCount;
this.carName = Name.from(carName);
}
public void moveCar(CreateRandomNumber createRandomNumber) {
if (createRandomNumber.generateRandomNumber() >= CAR_MOVE_BOUNDARY) {
moveCount++;
}
}
public int getMoveCount() {
return moveCount;
}
public String getCarName() {
return carName.getName();
}
}
Car 클래스에서 아쉬운건 moveCount 부분.. moveCount 원시값 포장한거 넘겨 받거나 아니면 생성자로 값 받아서 관리 해줄지 고민했는데 필드로 관리하였다.. 뭔가 아쉽. 여기서 CreatRandomNumber 클래스는 Web 패키지 하위에 있다. Random 값 생성해주는 클래스(CreateRandomNumber)를 나중에 Spring Api로 작성할 때 빈에 등록해야 했고, @Component 어노테이션을 붙여줌에 따라 패키지를 옮길 수 밖에 없었다 ㅠ 나중에 Spring APi 설명해줄 때 소개 해 드릴게여.
- CarNameParser
package com.racing.common.domain;
import com.racing.common.domain.vo.Name;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class CarNameParser {
private static final String SPLIT_STRING_DELIMITER = ",";
public final List<Name> carNames;
public CarNameParser(String carNames) {
this.carNames = parseCarName(carNames);
}
public List<Name> getCarNames() {
return carNames;
}
private List<Name> parseCarName(String carNames) {
String[] parsedCarNames = carNames.split(SPLIT_STRING_DELIMITER);
List<Name> Names = new ArrayList<>();
for (String carName : parsedCarNames) {
Names.add(Name.from(carName));
}
return Names;
}
}
차 이름 입력받았을 때 하나 하나 Name으로 원시값 포장 받아서 List<Name> 일급컬렉션 형태로 만들어줌.
- Car
package com.racing.common.domain;
import com.racing.common.domain.vo.Name;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class Cars {
private static final int INITIAL_NUMBER = 0;
private final List<Car> cars;
public Cars(List<Name> carNames) {
this.cars = makeCars(carNames);
}
public Cars(List<Car> carBundle, boolean dummy) {
this.cars = carBundle;
}
public List<Car> getCars() {
return cars;
}
public List<String> getWinner() {
return cars.stream()
.filter(this::isMaxCount)
.map(Car::getCarName)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
private boolean isMaxCount(Car car) {
return car.getMoveCount() == getMaxCount();
}
private int getMaxCount() {
return cars.stream()
.mapToInt(Car::getMoveCount)
.max()
.orElse(INITIAL_NUMBER);
}
private List<Car> makeCars(List<Name> carNames) {
List<Car> cars = new ArrayList<>();
for (Name carName : carNames) {
Car car = new Car(INITIAL_NUMBER, carName.getName());
cars.add(car);
}
return cars;
}
}
Car들을 관리하는 클래스. 역시 List<Car> 일급 컬렉션 형태로 만들어 줬고, Winner 뽑는 메서드도 구현해줬다.
*view 패키지
-InputView
package com.racing.console.view;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class InputView {
private final Scanner input;
public InputView(Scanner input) {
this.input = input;
}
public String inputCarNames() {
return input.next();
}
public int inputChance() {
return input.nextInt();
}
}
a
-OutputView
package com.racing.console.view;
import java.util.List;
public class OutputView {
public void inputCarNamesGuide() {
System.out.println("경주할 자동차 이름을 입력하세요(이름은 쉼표(,)를 기준으로 구분).");
}
public void getChanceGuide() {
System.out.println("시도할 회수는 몇회인가요?");
}
public void runGuide() {
separateLine();
System.out.println("실행결과");
}
public void showCar(String carName, int moveCount) {
System.out.println(carName + " : " + "-".repeat(moveCount));
}
public void separateLine() {
System.out.println();
}
public void showWinner(List<String> carWinners) {
System.out.println(String.join(",", carWinners) + "가 최종 우승했습니다.");
}
}
view 패키지들은 어디에도 의존하지 않도록 MVC 패턴 철저하게 지켜서 작성 (물론 domain 도 마찬가지임)
*Controller 패키지
- CarController
package com.racing.console.controller;
import com.racing.common.domain.*;
import com.racing.common.domain.vo.Name;
import com.racing.console.view.InputView;
import com.racing.console.view.OutputView;
import com.racing.web.random.CreateRandomNumber;
import java.util.List;
public class CarController {
private static final int INITIAL_NUMBER = 0;
private final InputView inputVIew;
private final OutputView outputView;
private final CreateRandomNumber createRandomNumber;
public CarController(InputView inputVIew, OutputView outputView, CreateRandomNumber createRandomNumber) {
this.inputVIew = inputVIew;
this.outputView = outputView;
this.createRandomNumber = createRandomNumber;
}
public void run() {
Cars cars = new Cars(getCarNames());
List<Car> carBundle = cars.getCars();
int moveCarChance = getChance();
outputView.runGuide();
moveCars(carBundle, moveCarChance);
outputView.showWinner(cars.getWinner());
}
private List<Name> getCarNames() {
outputView.inputCarNamesGuide();
CarNameParser carNameParser = new CarNameParser(inputVIew.inputCarNames());
return carNameParser.getCarNames();
}
private int getChance() {
outputView.getChanceGuide();
return inputVIew.inputChance();
}
private void moveCar(List<Car> carBundle) {
for (Car car : carBundle) {
car.moveCar(createRandomNumber);
outputView.showCar(car.getCarName(), car.getMoveCount());
}
outputView.separateLine();
}
private void moveCars(List<Car> carBundle, int moveCarChance) {
for (int i = INITIAL_NUMBER; i < moveCarChance; i++) {
moveCar(carBundle);
}
}
}
요론식으로 잘 조합해줬다.
- ConsoleApplication
package com.racing.console;
import com.racing.console.controller.CarController;
import com.racing.console.view.InputView;
import com.racing.console.view.OutputView;
import com.racing.web.random.CarRandomNumber;
import com.racing.web.random.CreateRandomNumber;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ConsoleApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
OutputView outputView = new OutputView();
InputView inputVIew = new InputView(scanner);
CreateRandomNumber createRandomNumber = new CarRandomNumber();
CarController carController = new CarController(inputVIew, outputView, createRandomNumber);
carController.run();
}
}
여기서 scanner 를 외부에서 주입받은 이유는 테스트 할 때, 이런식으로 외부에서 주입 받아주면 다른 입력 소스값을 넣어 줄 수 있어서 다양한 테스트 가능하고, 조금 더 객체지향적인 코드를 구현할 수 있어서 외부에서 주입받을 수 있도록 코드 구현해주었다.
느낀점.
확실히 초록스터디 미션을 하면서 실력이 많이 는 것 같다. 어떤식으로 코드를 작성해야 할 지 알게 되었고, 원시값 포장 일급컬렉션 같은 용어들에 대해 실습을 통해 확실하게 알 수 있었다. 앞으로는 Map, Optional 등 더 다양한 메서드와 자료구조 형태를 이용해보면서 java에 대한 이해를 한 층 높이고 싶다. 레이싱카 굿굿. 나중에 보면 왜 이렇게 작성했나 싶겠지만, 나름 지금 열심히 작성한 것...